Cannabinoids: Everything You Should Know
Written by Marijuana Cannaisseur on Aug 15, 2022
Cannabis is nothing new. However, with the ongoing debate about the benefits and drawbacks of cannabinoids and other cannabis compounds, it can seem as if cannabis is an emerging trend. The reality, of course, is that cannabis has been widely used for more than 5000 years, often for its medicinal properties. The plant has been rooted in American society since before the country’s beginning, as it was introduced by Native culture.
Cannabinoid Recognition
The medical field first began recognizing the benefits of the cannabinoid compounds within cannabis in 1850. However, by 1937, the federal government was challenging its use, implementing laws to restrict cannabis, and enacting legal penalties for its distribution. Unfortunately, this also meant that valuable research regarding the benefits of cannabinoid compounds came to a halt, delaying researchers from evaluating potential applications for cannabinoids as a therapeutic option.
It wasn’t until 1996 that California became the first state to reintroduce cannabinoids for medical purposes. Now, more states are not only allowing cannabis use for medicinal purposes but have started to retract cannabis criminalization laws. Many others have enacted full recreational legalization laws.1
We’ve come a long way since illegal cannabis, and it’s important to learn about the various cannabinoid effects and cannabinoid uses so that you can empower yourself to make informed choices.
What Are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds present within the cannabis plant that, when introduced to the body, interact with your natural endocannabinoid system (ECS) to boost its functions. The cannabinoids that are introduced through cannabis consumption can offer a boost to the analogous substances (endocannabinoids) that your body is already producing. Your body does this naturally to help maintain several functions:
- Hormone levels and fertility
- Heart rate
- Body temperature
- Hunger and digestion
- Immune function
- Hormone levels and fertility
- Heart rate
- Body temperature
- Hunger and digestion
- Immune function
When the body produces these endocannabinoids, they are present within body cells until they interact with and bind to a cannabinoid receptor. There, they either influence the receptor to take or stop taking a number of actions that regulate the above functions. There are two common types of receptors: CB1 (present mainly in the central nervous system) and CB2 (mainly present in the peripheral nervous system and the immune system). Because of the direct impacts of the ECS on the psychological and physical reactions listed above, it’s no wonder humans went in search of natural sources that could mimic these qualities.
With this in mind, you can think about cannabinoids in a similar way you may think of a vaccine or booster shot. While your body has a way of fighting off most viruses, sometimes it needs a little help—that’s why you receive vaccines from a doctor to prevent infection and medicine to treat infection. Similarly, the body’s ECS may need a little help regulating certain bodily functions, either due to its own inefficiencies or because disease processes have begun in the body.
The cannabinoids cannabis use introduces to the system bind with and activate the same receptors as our natural endocannabinoids. This is why the medical community is increasingly using cannabinoids as a way to treat a variety of issues pertaining to the ECS, both for physical and mental health.
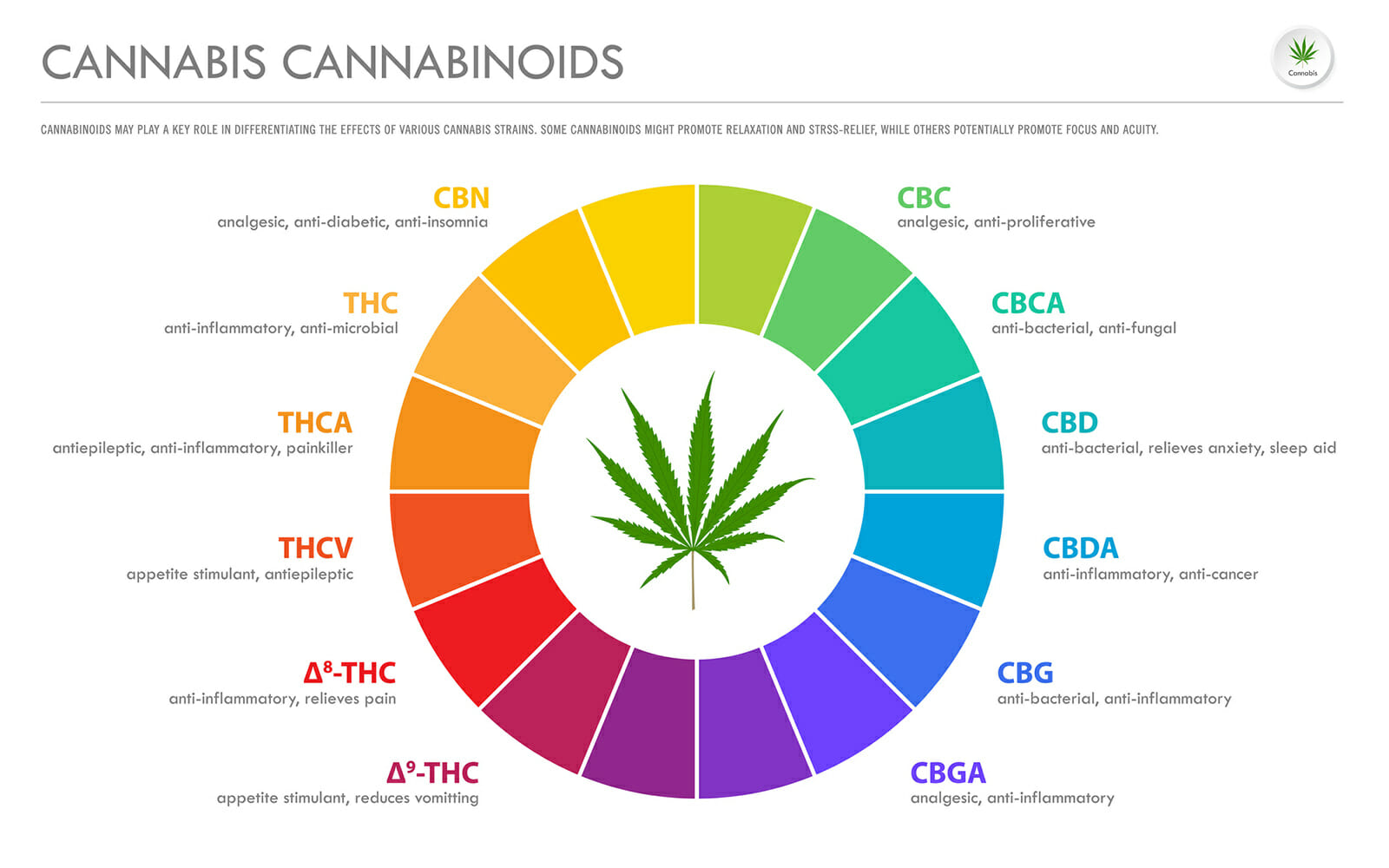
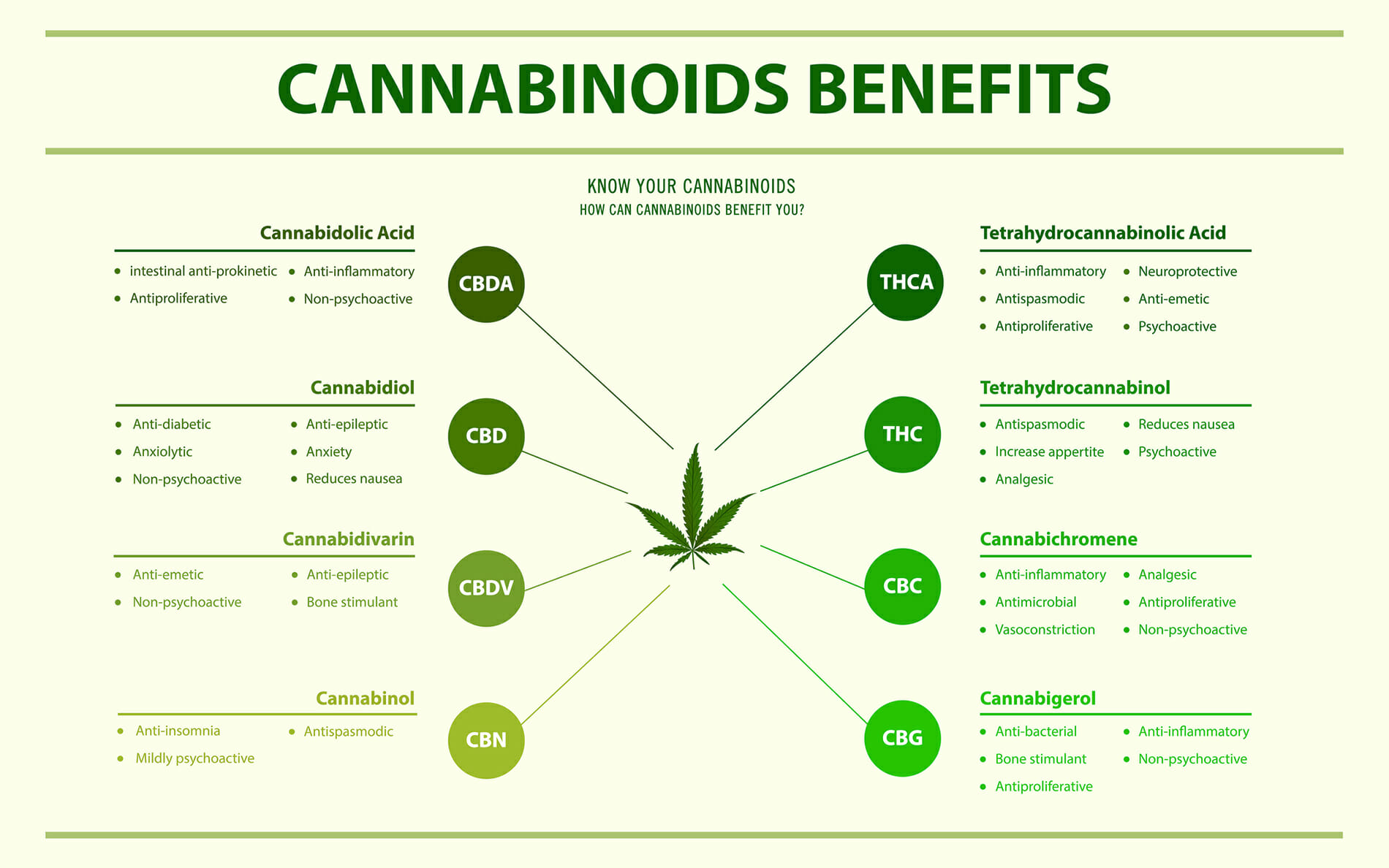
Types of Cannabinoids
Scientists have discovered over 400 different chemicals in cannabis with over 60 different types of cannabinoids. Chances are, you may only be familiar with the most prominent two: delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).2 We’ll keep our focus on these two.
Despite the fact that both THC and CBD have the same chemical formula, the way the atoms are arranged means that their interactions with—and effect on—the ECS are very different. For example, THC is the compound behind the “high” feeling a person experiences after consuming cannabis because of its psychoactive properties. CBD is not psychoactive, but is linked to feelings of well-being through its antipsychotic, anxiolytic, antiepileptic, and anti-inflammatory properties.3 Another cannabinoid, CBN, is a derivative of THC and can have some psychoactive effects that are not intoxicating.
THC can bind to both CB1 and CB2 receptors, which is believed to be the mechanism behind its psychoactive abilities since CB1 receptors are prevalent in the brain. THC functions as an agonist, which forces the receptor to begin a physiological response. By contrast, CBD is an antagonist, which serves to limit the interactions of other cannabinoids and endocannabinoids with the body. For this reason, the impact of a strain of cannabis on your body is dependent on the ratio of THC to CBD in that strain. Since CBD is known to reduce the impacts of THC, it can balance cannabis’ effects. The outcome (euphoria vs. simple well-being) will be determined by the ratio of these cannabinoids to one another. Adjusting this balance is how researchers can manipulate cannabis strains to have their particular impacts on the brain and body.
Cannabinoid Uses
Cannabinoids have a wide spectrum of uses, including:
Pain Relief
Studies suggest that cannabinoids may help provide pain relief,4 particularly for cancer patients. Cannabinoids may also help those with neuropathy, as well as other types of chronic and acute pain, by interacting with ECS receptors that regulate pain perception. Cannabinoids could also reduce inflammation in the body, a leading cause of pain.
Anti-Nausea/ Appetite Booster
Patients often experience a loss of appetite resulting from HIV/AIDS and other conditions. Cannabinoids have long been used reduce nausea and increase feelings of hunger. They may also influence maintenance of healthy metabolic hormones,5 which ensure food consumed is used to create energy to maintain other bodily systems. With these measures combined, patients can maintain a healthy weight and maximize the nutrients they receive from a healthy diet.
Anxiety Relief
CBD has already seen extensive use as an anti-anxiety agent. Now, researchers believe THC may help to mitigate anxiety at low doses. When used in the correct ratio, the two cannabinoids together can effectively reduce symptoms of anxiety.6
PTSD Relief
As an anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is certainly treatable with CBD, THC, or a combination of both cannabinoids. These compounds may also help to reduce the frequency of intrusive thoughts and nightmares commonly associated with the condition. In addition, PTSD patients report an increased ability to socialize and self-soothe after using cannabinoids.7
Insomnia and Sleep Disorder Treatment
The link between cannabinoids and sleep regulation is well-documented. Cannabinoids, CBD in particular, appear to help study participants fall asleep more easily and more quickly, stay asleep longer, and achieve better sleep quality. With better sleep may come a reduction in anxiety, an improvement in mood, better concentration, and overall better health.8
This list is just a small portion of the uses researchers have discovered for cannabinoids. As more states legalize the use of medicinal and recreational cannabis and the federal government approves more extensive laboratory study, research will continue to find new uses and breakthroughs. It is important to note that cannabinoids won’t cure a disorder or disease. They will, however, help to minimize the symptoms of such disorders. When comparing the above list to the list of functions your body’s ECS controls, it is easy to see the potential for cannabinoid effects to act as an enhancement to the natural regulation already taking place inside the body.
Other Cannabinoid Uses

There are ongoing studies to show cannabinoids’ potential as an therapy for alleviating symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, Parkinson’s, and Crohn’s disease. There was a common belief that cannabinoids can help alleviate glaucoma symptoms, and this usage continues to be studied. Ongoing studies also reveal a potential for cannabis use to boost mood, reduce opioid withdrawal symptoms, and even inhibit opioid use. These and many other research opportunities highlight a bright future for therapeutic cannabinoid use.
Another important factor to consider is that cannabinoids may serve as a safe alternative for many existing opioid medications. Opiates are arguably more addictive and harmful, but are widely prescribed to many patients who need help with pain management. Cannabinoids are substantially less addictive, also work to treat pain in many patients, and do not harbor the same overdose risk as common opioids. When comparing the use of cannabis to that of opioids in states where cannabis is offered medically, prescription rates for not only opioids but other drugs that cannabis could replace were significantly lower.9
Synthetic Cannabinoids
Because of the increased interest and production in the medical field of both natural and synthetic forms of cannabinoids, the FDA has conducted its own research and has weighed in on the issue. One natural and three synthetic products have been officially approved by the FDA and are available through prescription. These cannabinoid-based products are:
- Epidiolex (CBD)
- Marinol
- Syndros
- Cesamet
You might think that because it is governmentally regulated, these products are in a very basic form. However, you may be surprised to know that at least two of the products, Marinol and Syndros, contain the ingredient dronabinol, which is a synthetic form of THC. These two drugs, in particular, are used in association with chemotherapy and anorexia. The final synthetic product, Cesamet, is used similarly to the previous two but uses an active ingredient called nabilone which is chemically structured to mimic THC.10
The Future for Cannabis

The long, complicated history of cannabinoids has clouded fact and fiction. However, the health benefits of this natural, sustainable source are numerous. As research continues, we will likely discover even more benefits and uses for cannabis products. As it currently stands, you can find medical cannabinoid products in 37 states, with more considering recreational and medical legalization on the horizon.
More strains are available than ever before, and those that enjoy smoking or vaping cannabis will likely find a strain to match almost any of the above conditions. Of course, not everyone likes to inhale their cannabis. The great news is that cannabis is available in an almost infinite number of varieties, from tasty edible products and flavored beverages to an assortment of topicals, sprays, tinctures, and so much more.
We don’t know if the debate will ever end, and maybe it shouldn’t. As long as people continue to challenge one another in constructive ways, we will push each other to continue research and innovation. In the meantime, it’s important to continue to educate and inform to make sure those conversations are grounded in the facts about cannabinoids and not in the rumors. As we continue to watch the development of cannabinoids, we will continue to remain on the front lines, arguing for their benefit.
Medical and Recreational Cannabis in Arizona
Interested in trying out the benefits of cannabinoids for yourself? At Kind Meds, our team has the knowledge and experience to help you understand cannabinoids and how they can help you. We will walk you through our selection of high-quality products so that you can make the decisions that are right for you. At our boutique dispensary, you’re sure to find a product and a strain that’s perfect for your needs. Stop in today, or contact us with any questions or concerns.